Shrinkage film is a thermoplastic film that is stretched and oriented during production and shrinks during use. Therefore, no matter which printing method is used for printing, before designing the surface pattern, it is necessary to consider the transverse and longitudinal shrinkage rates of the material, as well as the allowable deformation errors in various directions of the decorative graphics and text after shrinkage, in order to ensure the accurate restoration of the patterns, text, and barcodes shrunk onto the container.
1. Direction of pattern
Regardless of whether the heat shrinkable film is printed in intaglio or flexographic printing, its printing is mainly in the form of inner printing, and the direction relative to the pattern on the printing plate should be positive. Nowadays, there are also surface printed shrink films. If this happens, the pattern direction on the printing plate should be reversed.
2. Hierarchy of patterns
Due to the disadvantages of flexographic printing, if the shrink film is flexographic printing, the level of the image should not be too delicate, while using gravure printing can require a richer level of image. 3. Design of dimensions
The lateral shrinkage of the heat shrinkable film material used for printing is 50% to 52% and 60% to 62%, which can reach 90% under special circumstances. The longitudinal shrinkage is required to be 6% to 8%. However, during the instantaneous contraction of the film, due to the limitations of the container, the horizontal and vertical shrinkage cannot be fully achieved. To ensure the accurate restoration of the shrunken pattern, text, and barcode, it is necessary to take into account the shape of the container and calculate the correct size and deformation rate based on the actual situation. For heat shrinkable labels that need to convert a sheet like film into a cylindrical shape and use adhesive to seal the overlapping parts together, it is important to note that no graphics and text are generally designed at the sealing part to avoid affecting the adhesion fastness.
4. Barcode placement
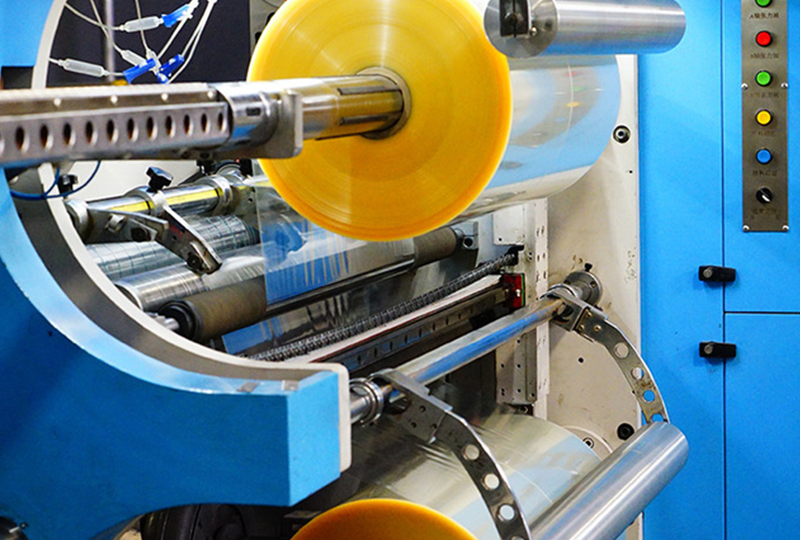
Generally, the placement direction of the barcode should be consistent with the direction during printing, otherwise the lines of the barcode will be distorted, which will affect the scanning results and cause misreading. In addition, the color selection of label products should focus on spot colors as much as possible, and the production of a white version is necessary, which can be made into a full version or hollow out according to the actual situation. The color of bar codes should comply with the conventional requirements, that is, the color matching of bars and blanks should comply with the color matching principles of bar codes. Selection of printing materials. The printing of heat shrinkable labels has been briefly analyzed above. In addition to controlling the printing process, materials play a decisive role in affecting their quality. Therefore, selecting the right material is the key. The thickness of the film material is determined based on the application field, cost, film characteristics, shrinkage performance, printing process, and labeling process requirements of the heat shrinkable label. Generally, the film thickness for making shrink film labels should be between 30 microns and 70 microns, with 50 microns, 45 microns, and 40 microns being more commonly used, depending on the labeling performance of the labeling device. For selected label materials, it is generally required that the shrinkage of the film material be within the application range, and that the lateral (TD) shrinkage be higher than the longitudinal (MD) shrinkage. The lateral shrinkage of commonly used materials is 50% to 52% and 60% to 62%, and can reach 90% under special circumstances. The longitudinal shrinkage is required to be between 6% and 8%. In addition, as the shrink film is very sensitive to heat, it is important to avoid high temperatures during storage, printing, and transportation


 当前位置:
当前位置:

 热门推荐
热门推荐
























 联系人:庞经理
联系人:庞经理